Expression Rule
An expression rule is a reusable expression that can be referenced in other expressions. You can define rule inputs within it, allowing the output of the expression to change dynamically based on the input values.
This page provides guidance on how to create, modify, and remove expression rules.
Create
To create an expression rule:
- In your application go to application view, select an application and either click on the application name or go to object view.
- Click the Create New drop down and select Rule.
- Configure the following properties:
- Name
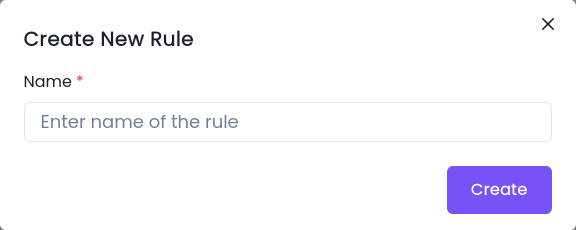
- Click create.
The expression rule opens in a new dialog or window, where you can:
- Add input body.
- Pass test inputs.
- Pass parameters.
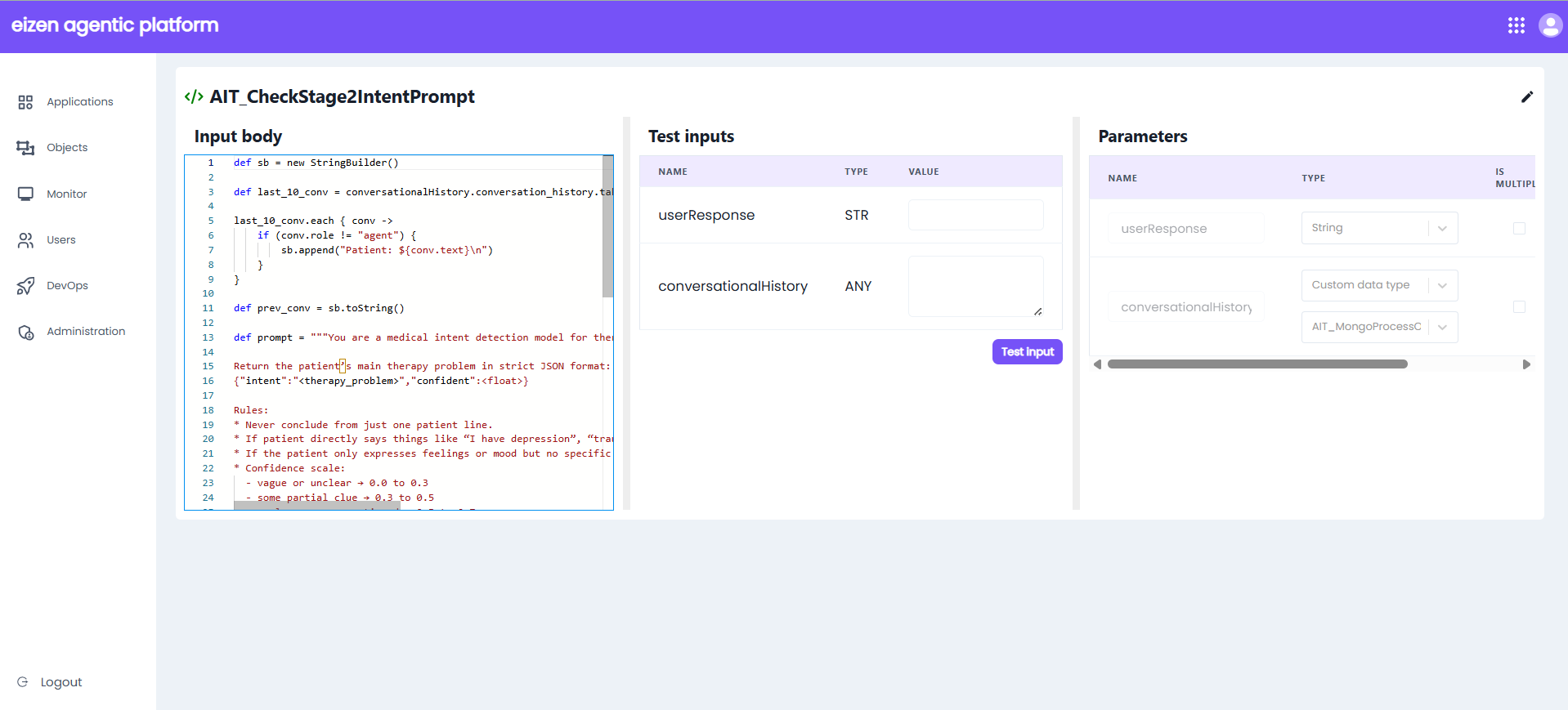
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Body | The Input Body is a scripting area where you write Groovy code that will be executed when the rule or node runs. |
| Test Inputs | This panel shows all the input variables (if any) that are defined for the integration or rule. You would normally see: - Name of the input - Type (e.g., Text, Integer, CDT, etc.) - Value (where you manually input a test value) |
| Parameters | This section lists any parameters required by the rule/integration. These are typically: - Static or dynamic configuration values. - Record fields, booleans, strings, or dates. Columns: - Name: The name of the parameter. - Type: Data type of the parameter (e.g., String, CDT, etc.). - Is Multiple: Indicates if this parameter accepts an array/list of values. - Order: Execution or input order, if applicable. |
Using Custom Data Type in Parameters :
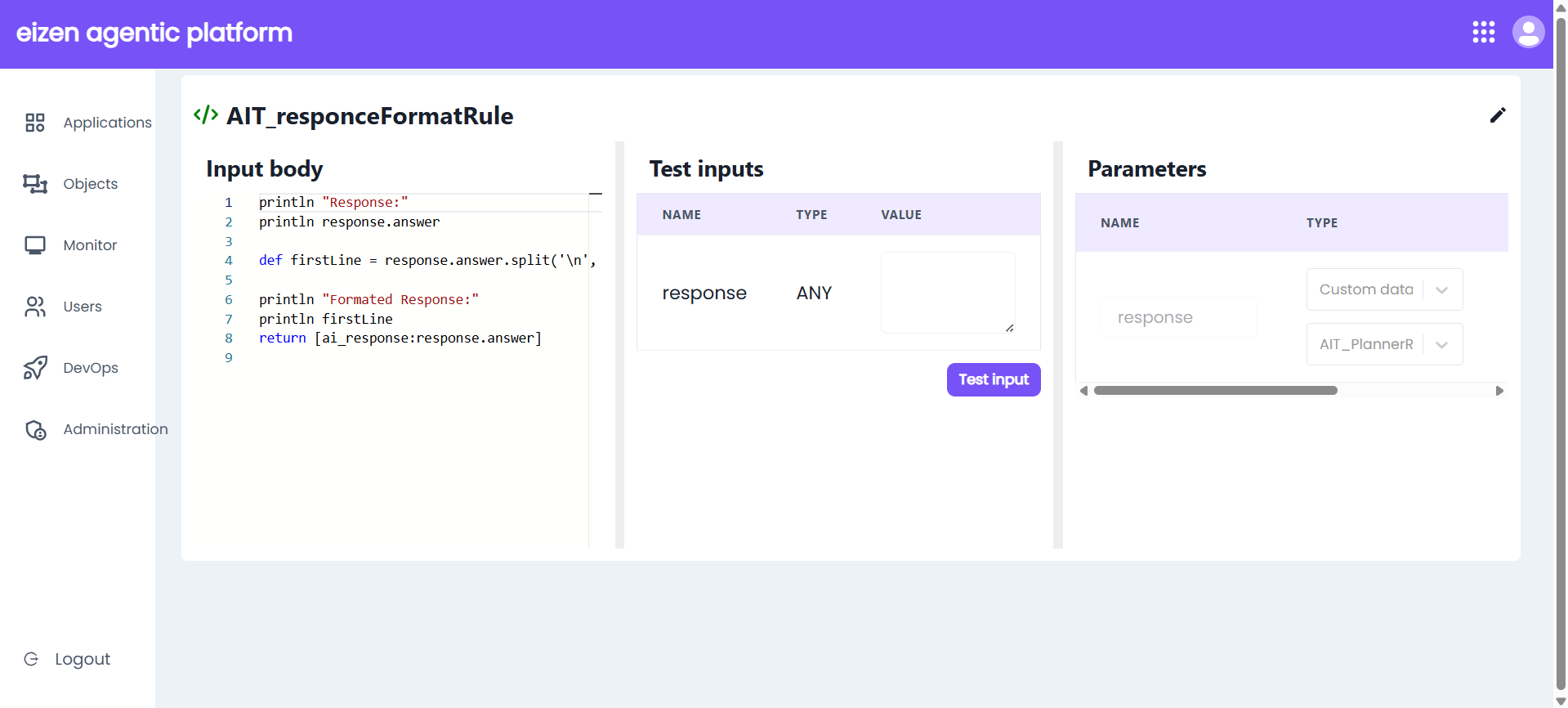
- Custom Data Types can be selected as parameters in an Expression Rule, allowing you to define structured inputs instead of plain values.
- While adding a Test Input, you can pass values in JSON format for the Custom Data Type, which makes it easy to test rules with complex structured data.
Rule for User Record(Database) :
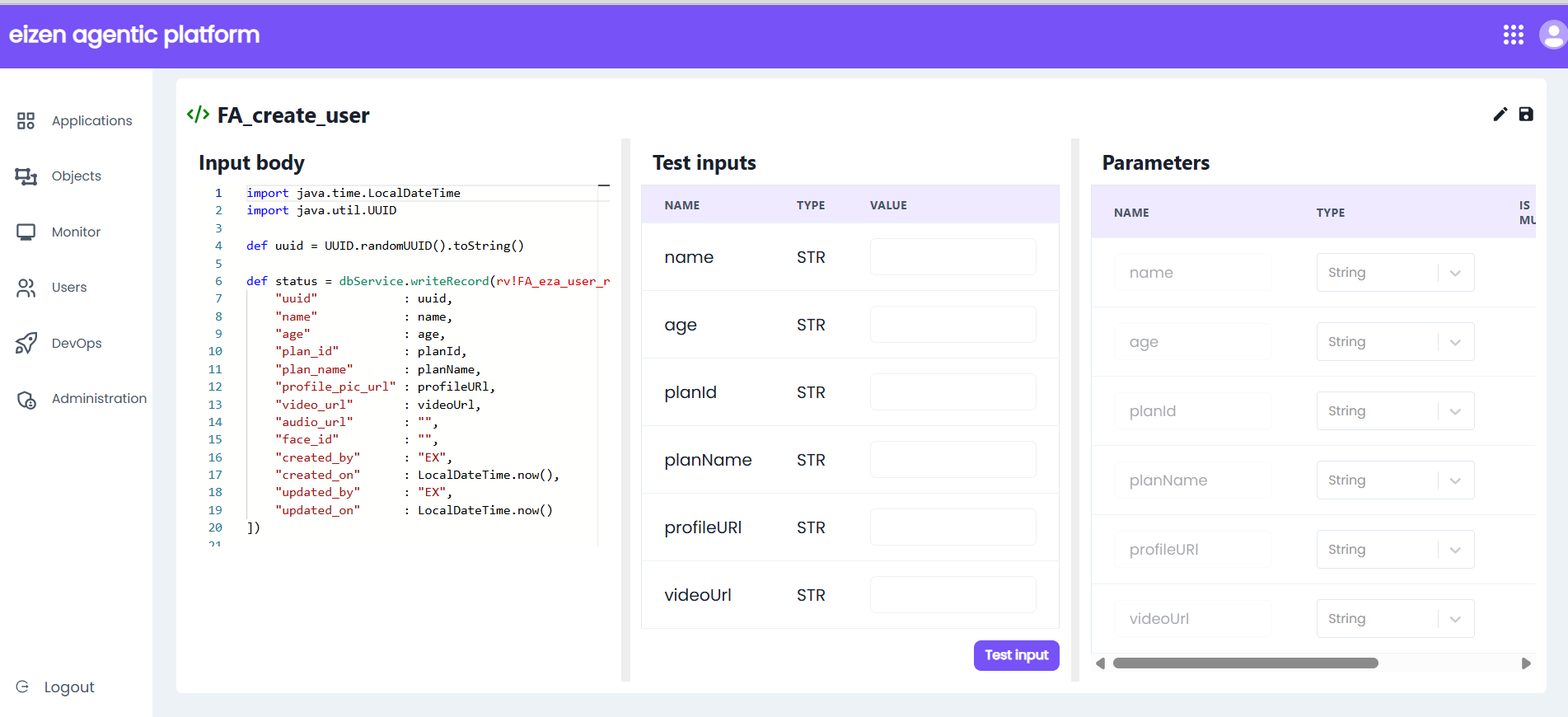
- This rule demonstrates how we can write and retrieve data from the database using a defined record type. Key Points
Database Interaction:
-The function dbService.writeRecord() is used to store a record into the database.
-The first parameter rv!FA_eza_user_r refers to the record type in which the data will be stored.
rv! (Rule Variable):
rv!stands for Rule Variable.- It represents the record type or data structure linked to this rule.
Example: rv!FA_eza_user_r points to the record type FA_eza_user_r where user information is saved.
Data Being Stored:
- User-specific fields such as
name, age, planId, planName, profileUrl, and videoUrl. - Metadata fields such as
uuid, created_by, created_on, updated_by, and updated_on.
Record Type:
- A record type acts like a table structure in the database.
- Each time this rule runs, it inserts a new record in the corresponding record type with the given attributes.
dbService Methods:
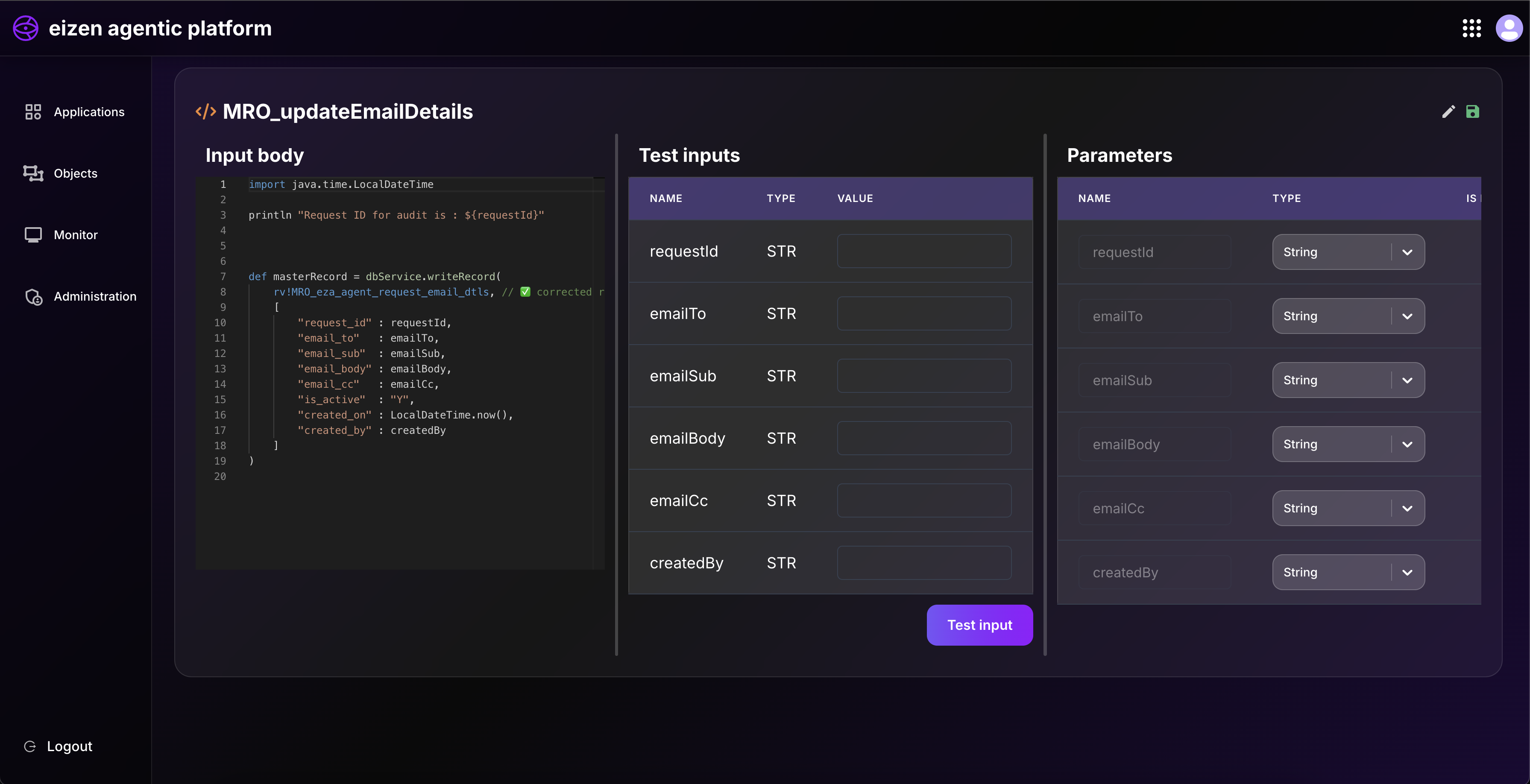
dbService.writeRecord() → Insert new record
- Used to add a new row into a table.
- You pass the table name and a map of column values.
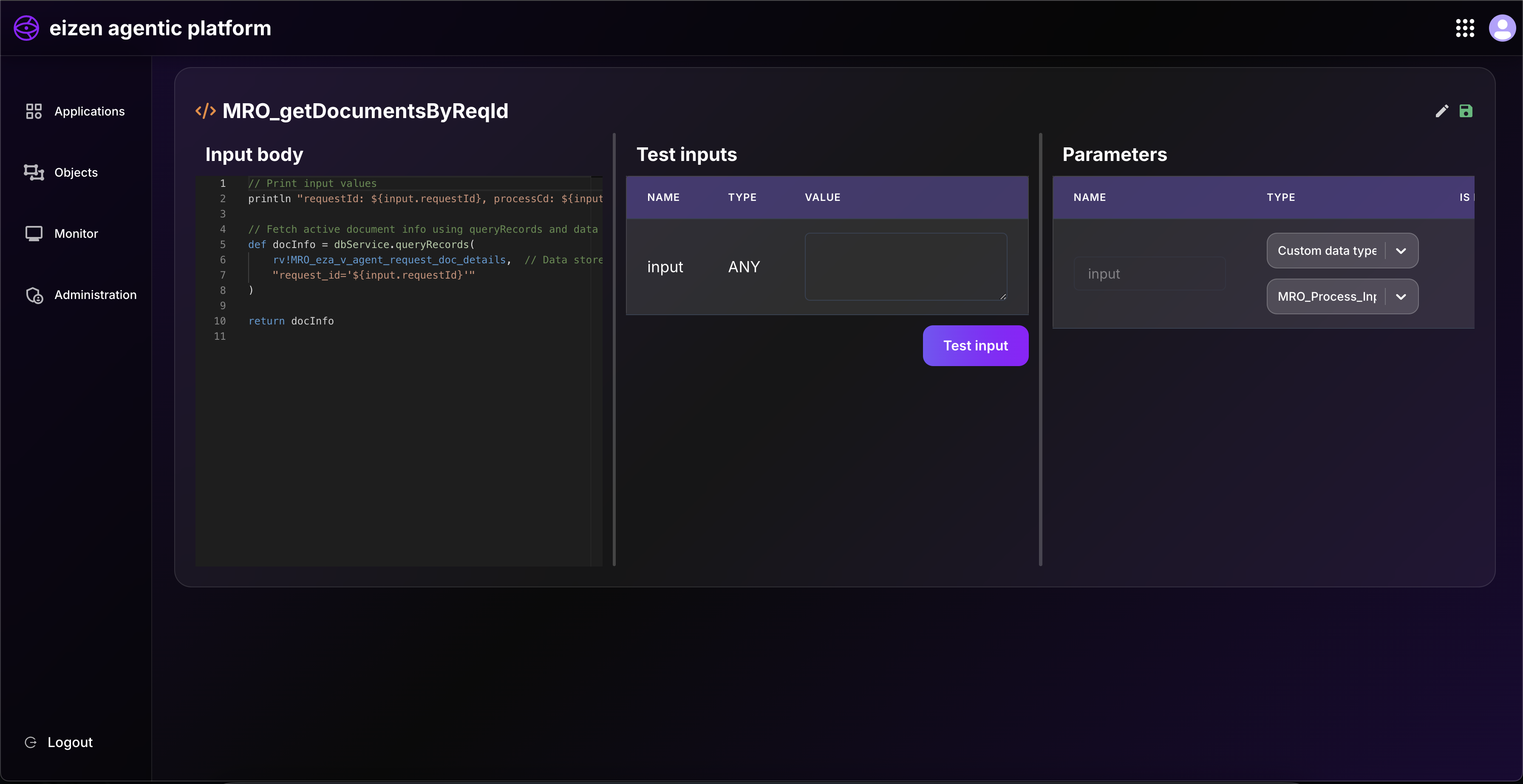
dbService.queryRecords() → Fetch multiple records
- Returns a list of rows matching given criteria.
- Useful when you expect more than one result.
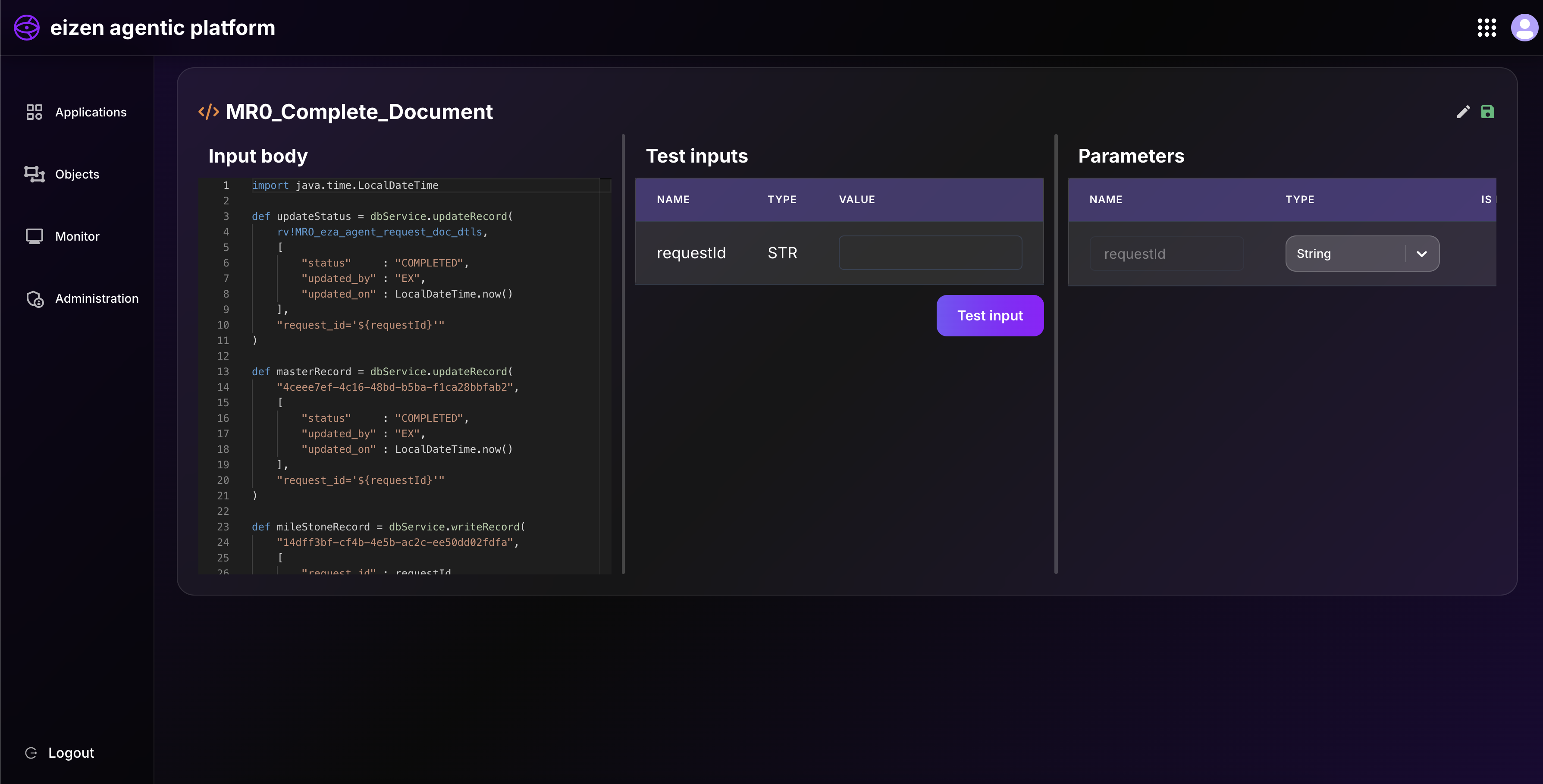
dbService.updateRecord() → Update existing record
Modifies an existing row in the table.
You specify which record and provide new values.
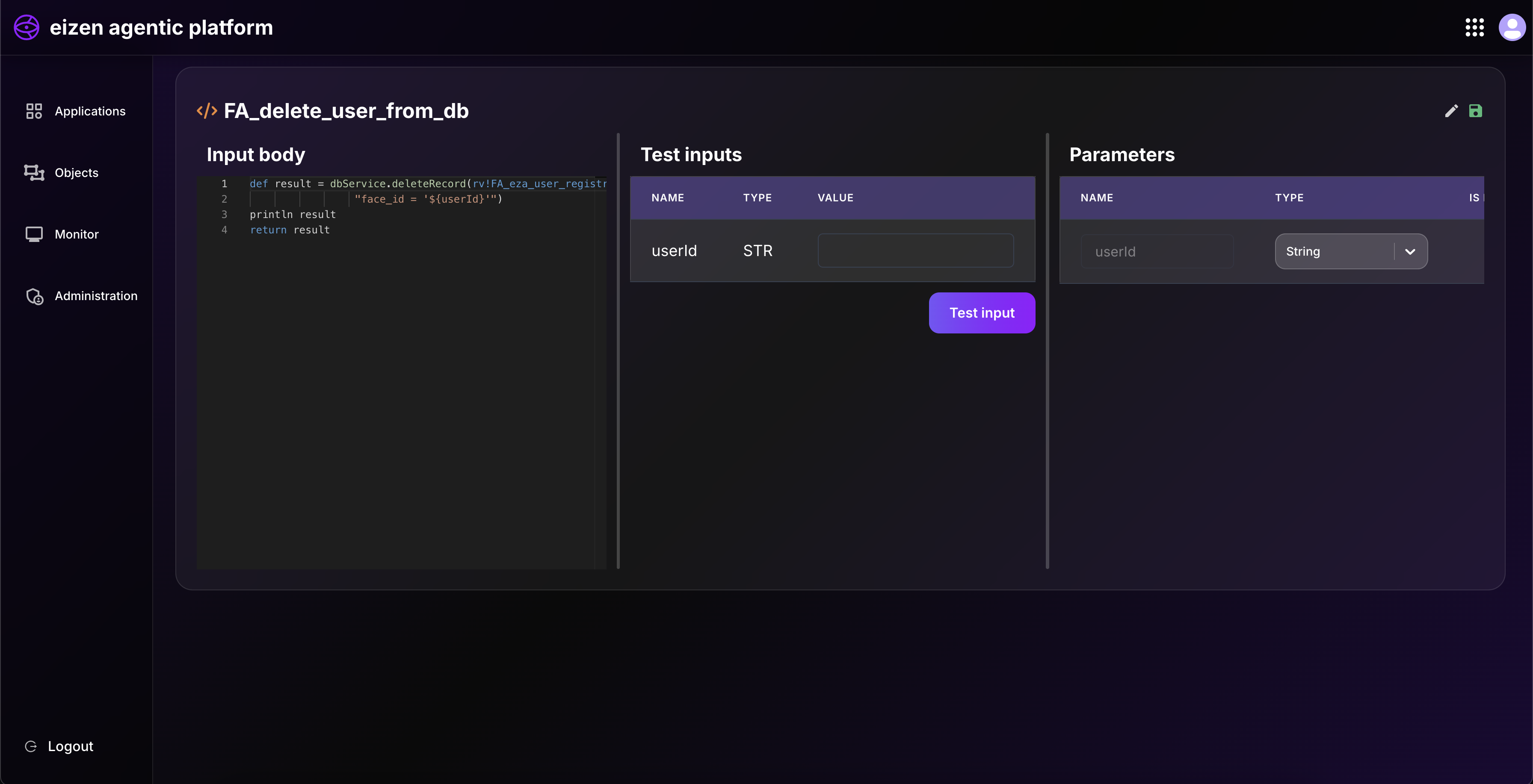
dbService.deleteRecord() → Delete record by key
Removes a row from the table using a key.
Deletes only the specified record, not all.
Test Inputs:
- On the right side, we define test input variables such as:
name, age, planId, planName, profileUrl, videoUrl.
These values can be passed dynamically and tested through the UI.